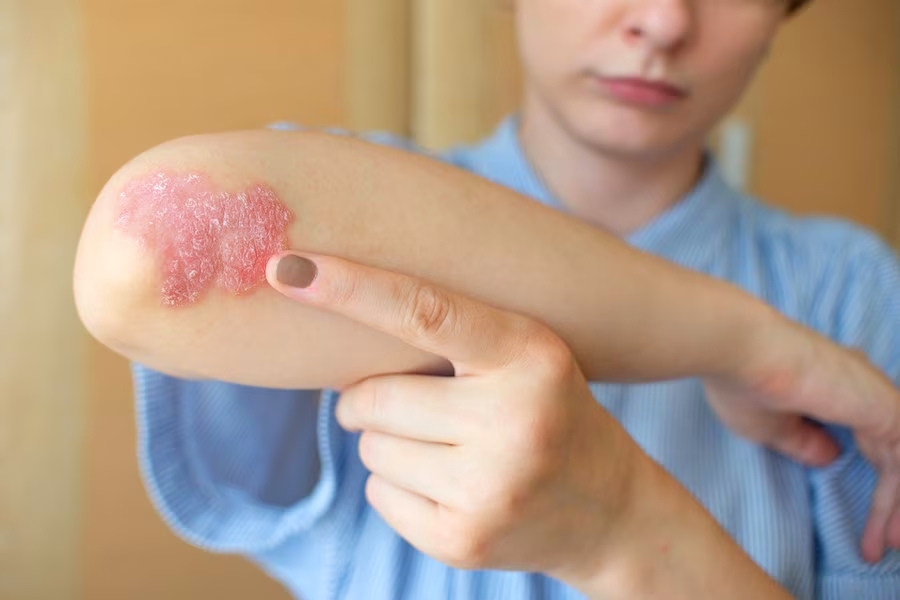
Plaque psoriasis is a chronic skin condition characterized by the rapid build-up of skin cells, leading to the formation of thick, red, and scaly patches on the skin’s surface. While plaque psoriasis has no definitive cure, managing its symptoms involves a holistic approach that includes lifestyle choices, dietary considerations, and targeted treatments. In this comprehensive guide, we will explore five foods to avoid for individuals with plaque psoriasis and delve into various treatment options available to enhance the quality of life for those affected by this skin condition.
Foods to Avoid with Plaque Psoriasis:
- Processed Foods and Sugars:
Processed foods and those high in added sugars have been associated with inflammation, which can exacerbate plaque psoriasis symptoms. Diets rich in processed snacks, sugary beverages, and sweets may contribute to an inflammatory response in the body, potentially triggering or worsening psoriasis flare-ups. Alternative: Opt for whole, nutrient-dense foods, such as fruits, vegetables, lean proteins, and whole grains. These choices can provide essential vitamins and minerals while minimizing the inflammatory impact on the body. - Red Meat and Dairy:
Certain proteins found in red meat and dairy products may contribute to inflammation and worsen psoriasis symptoms for some individuals. While not everyone with psoriasis is affected by these proteins, it’s advisable to monitor personal reactions and consider reducing the consumption of red meat and dairy if flare-ups coincide with their intake. Alternative: Explore plant-based protein sources like legumes, nuts, and seeds, and consider incorporating non-dairy alternatives like almond or oat milk. These alternatives can be part of a well-rounded diet that supports skin health. - Gluten-Containing Foods:
Some individuals with psoriasis may experience improvements in their symptoms by avoiding gluten, a protein found in wheat, barley, and rye. While the relationship between gluten and psoriasis varies among individuals, exploring a gluten-free diet may be worth considering, especially for those who notice a correlation between gluten intake and flare-ups. Alternative: Choose gluten-free grains like quinoa, rice, and gluten-free oats. Experimenting with gluten-free alternatives can help identify whether gluten plays a role in exacerbating psoriasis symptoms. - Nightshade Vegetables:
Nightshade vegetables, including tomatoes, eggplants, peppers, and potatoes, contain alkaloids that may contribute to inflammation in some individuals. While the impact of nightshades on psoriasis varies, some people report improvements in symptoms after limiting their intake. Alternative: Opt for alternative vegetables such as leafy greens, carrots, and squash. These alternatives offer a range of nutrients without the potential inflammatory effects associated with nightshades. - Alcohol:
Excessive alcohol consumption has been linked to an increased risk of psoriasis and may worsen existing symptoms. Alcohol can contribute to inflammation in the body and may interfere with certain psoriasis treatments, making it advisable for individuals with plaque psoriasis to moderate their alcohol intake. Alternative: If choosing to consume alcohol, moderation is key. Opt for lower-alcohol beverages and stay hydrated to minimize the potential impact on psoriasis symptoms.
Treatment Options for Plaque Psoriasis:
- Topical Treatments:
Topical treatments are often the first line of defense against plaque psoriasis. These include corticosteroids, vitamin D analogs, and topical retinoids. These medications work by reducing inflammation, slowing down the growth of skin cells, and promoting normal skin cell turnover. Application: Apply topical treatments directly to affected areas, following your healthcare provider’s recommendations. Consistency in application is crucial for optimal effectiveness. - Phototherapy (Light Therapy):
Phototherapy involves exposing the skin to ultraviolet (UV) light under controlled conditions. Both natural sunlight and artificial UV light can be used to manage psoriasis symptoms. Phototherapy is particularly effective for widespread psoriasis or when topical treatments alone may not be sufficient. Procedure: Phototherapy is typically administered in a healthcare setting, either with a lightbox or exposure to natural sunlight. It’s important to follow the recommended treatment schedule to achieve the desired results. - Systemic Medications:
For more severe cases of plaque psoriasis, systemic medications may be prescribed. These medications work throughout the body to suppress the immune system’s overactive response that leads to psoriasis symptoms. Systemic medications include oral medications and biologics. Administration: Oral medications are taken by mouth, while biologics are often administered through injections or infusions. Close monitoring by healthcare providers is crucial due to the potential side effects of systemic medications. - Lifestyle Modifications:
Certain lifestyle changes can complement medical treatments and promote overall skin health. Managing stress, staying hydrated, and avoiding known triggers can contribute to minimizing psoriasis symptoms. Additionally, maintaining a healthy weight through regular exercise and a balanced diet can positively impact psoriasis management. Incorporation: Integrate stress-reducing activities such as yoga, meditation, or mindfulness into your routine. Stay hydrated by drinking an adequate amount of water, and be mindful of personal triggers to prevent flare-ups. - Biologics:
Biologics are a type of systemic medication that specifically targets the immune system’s inflammatory response. They are often prescribed for moderate to severe plaque psoriasis that hasn’t responded adequately to other treatments. Biologics are administered through injections or infusions. Administration: Biologics are administered at specific intervals, as determined by your healthcare provider. Regular